2. Food systems and spread of diseases
Syllabus Link: How physical and human processes lead to changes in food production and consumption, and incidence and spread of disease
Recommended Videos
|
|
|
|
The merits of a systems approach
The merits of a systems approach (inputs, stores, transfers, outputs) to compare energy efficiency and water footprints in food production, and relative sustainability in different places
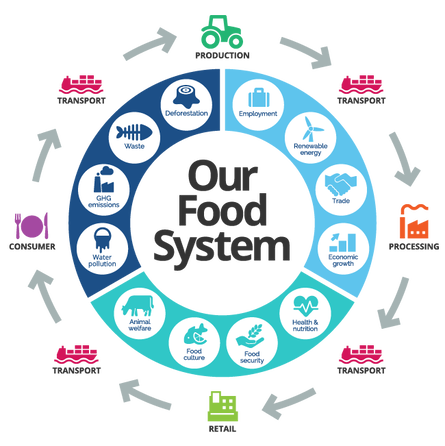
Food systems
|
|
|
|
Article: The hidden water resource
Article: Food's big water footprint
Article: How to make the food system more energy efficient
Slides: Sustainable agriculture
Energy efficiency
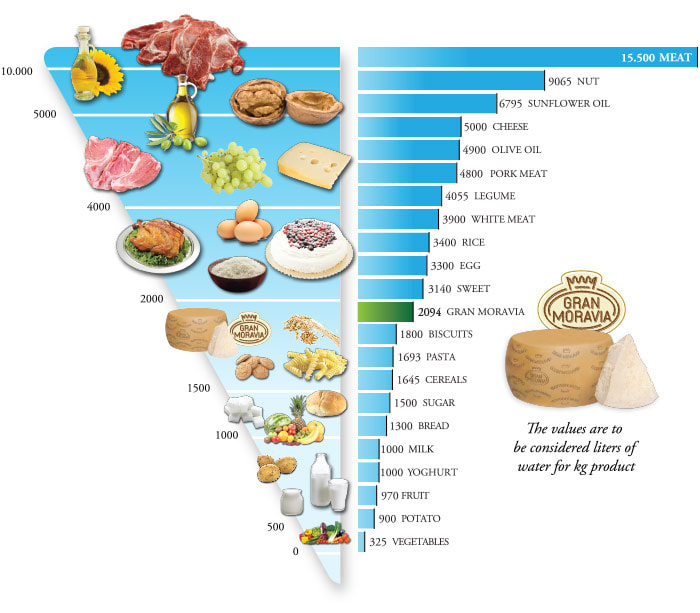
Water footprints
|
|
|
|
Relative sustainability
|
|
|
Webpage: Nat Geo - Is America's hunger for meat bad for the planet?
Visualizations: Sustainable diets - What you need to know
Lesson Plan: The circular economy and modern agriculture
Reading: Why worrying about food miles is missing the point
|
|
|
|
Physical and human processes
Physical and human processes that can lead to variations in food consumption
|
|
|
|
Activities: Factors that impact food consumption notes
Data: Visualizations of food per person
Reading: Global food consumption patterns and trends
|
|
|
The importance of diffusion
The importance of diffusion (including adoption/acquisition, expansion, relocation) in the spread of agricultural innovations, and also in the spread of diseases, and the role of geographic factors (including physical, economic and political barriers) in the rate of diffusion
The diffusion of agricultural innovations
|
|
|
|
Activities: Diffusion of Food Innovation Notes
Webpage: Agricultural productivity and innovation
Article: 20 Success stories of agricultural innovation
Reading: Nat Geo - The next Green Revolution
The Green Revolution
|
|
|
|
The Diffusion of Disease
The importance of diffusion (including adoption/acquisition, expansion, relocation) in the spread of diseases, and the role of geographic factors (including physical, economic and political barriers) in the rate of diffusion
|
|
|
|
|
Geographic Factors of Disease
Geographic factors contributing to the incidence, diffusion and impacts (demographic and socio-economic) of vector-borne and water-borne diseases
|
|
|
:
Instructions: Geographic factors of disease detailed example presentations
Reading: HIV - Example of the impacts of a disease
Presentations: Class presentation links
Instructions: Geographic factors of disease detailed example presentations
Reading: HIV - Example of the impacts of a disease
Presentations: Class presentation links